International Leader In Functional Medicine
Bellissimo Medical in Weston and Miami, Fl.What is Plaquex?
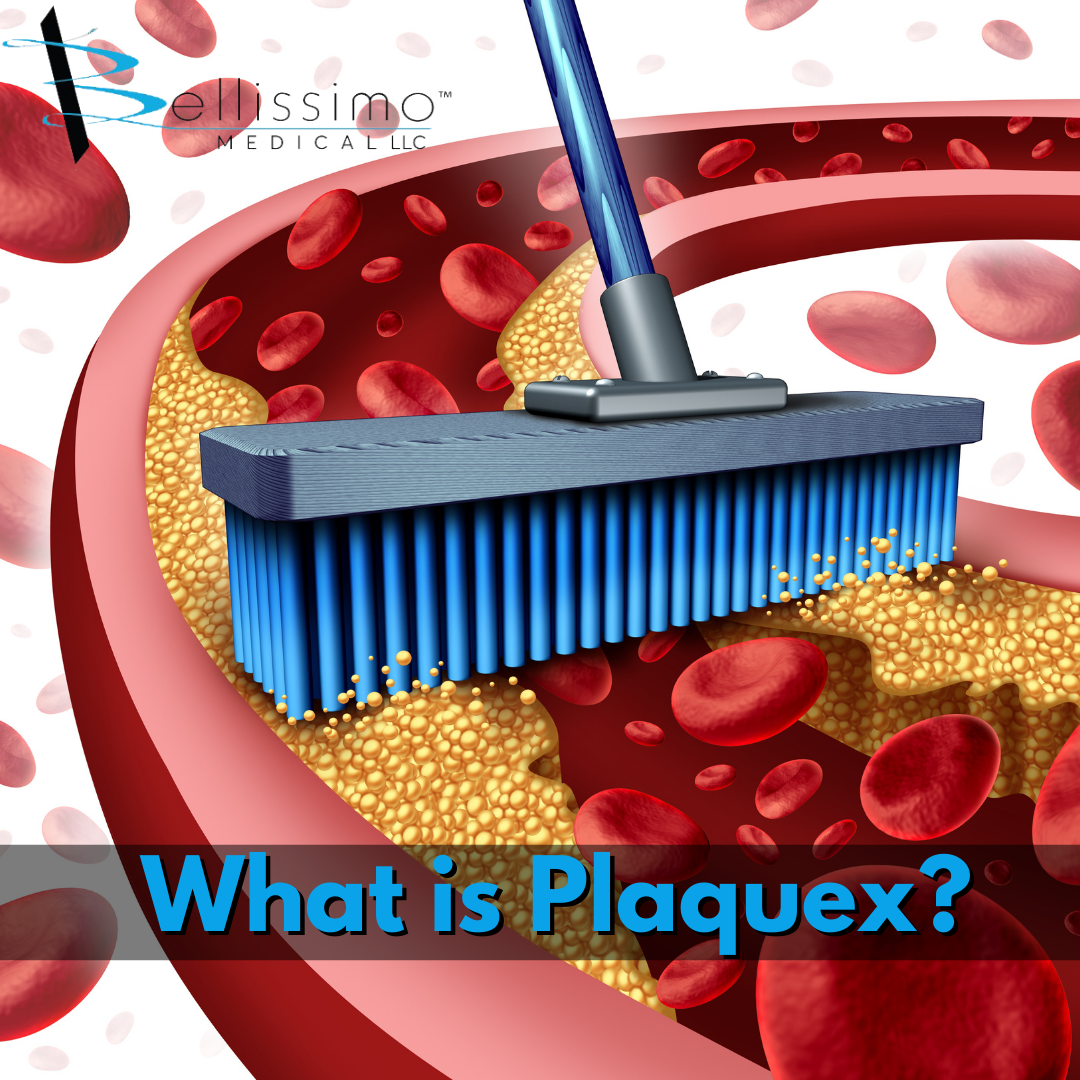
Plaquex is a mix of essential phospholipids (Phosphatidyl Cholines or Lecithins) derived from soybeans. As the name implies, Plaque-ex (rid off) is a natural statin that works like a broom, removing cholesterol from the blood and plaque from arteries, as well as repairing cell membranes and many other benefits.
Developed in Europe, Plaquex has been used successfully for over 60 years. Phospholipids are produced naturally by our organism, but as we age, the production declines, and the amount in our cell membranes decreases dramatically, or get damaged by toxins exposure, environmental contamination, sugar, smoking, free radicals, hypertension, and stress hormones.
Plaquex is effective for the following conditions:
- Coronary Artery disease
- Elevated Cholesterol
- Cell membrane repair
- Erectile dysfunction
- Kidney function
- Brain function
- Fatty Liver
- Hypertension
- Energy
- Skin
Independent studies have shown that LDL (Low-density Lipoprotein) can be reduced by as much as 30%, triglycerides by 25%, and HDL (High-density Lipoprotein) increased by 45% in a twelve-month period.
Plaquex can be administered in two forms:
- Orally (capsules)
- Intravenously (IV)
The administration form depends on the treatment protocol recommended by Dr. Jean-Claude Nerette.
Depending on the patient’s condition, he may also recommend heavy metal testing and/or chelation therapy since both treatments work simultaneously.
If you are experiencing any of the above health issues, call Dr. Jean-Claude Nerette, Jr. for a complimentary consult and experience the restorative power of Plaquex, the natural statin.
References.
Elevation of HDL, LDL, and liver enzymes at the beginning, which normalize with continuing treatment
Leuschner, F. A. Leuschner. Research report no. 0050/84 of December 27, 1983
Maeda, A. et al. Gendai no Shinryo 22 (1980) 189-192 and 1461-1465
Fasoli, A. Therap. Select. Risk/Benefit Assess. Hypolipid. Drugs
G. Ricci et al. (eds.) Raven Press: New York 1982, 257-262
Suo, T. et al. Kiso to Rinsho 15 (1981) 3046-3051
Belousova, S.S. et al. Kardiologiya 25 (1985) 112-115
Izumi, H. et al. 11th Proceed Jap. Atheroscl. Socl, Tokyo 1979
Nakamura, H. et al. Jap J. New. Rem. Clin. 22 (1973) 1565-1575
Spigai, C. Med. Heute 19 (1970) 197-198
Thurnherr A. Therapiewoche 7 (1956) 116
Friehe, H., R. Fontaine Report no. 840160 of December 16, 1978
Arsenio, L. et al. Clin. Ter. 114 (1985) 117-127
Tomasevic, M. Unpublished report no. 842746
Takahashi, S. Shinryo to Shinyaku 17 (1980) 3051-3064
Blagosklonov, A.S. et al. Kardiologiya 26 (1986) 35-38
Liver disease
Salvioli, G. et al. Il Fegato 21 (1975) 5-25 and: 4th Int. Sympos. Atheroscl., Tokyo 1976 and: Diab. Obes. Hyperlipoprot., Cupaldi, V. et al. (eds.), Academic Press: New York 1987
Salvioli, G. Scand J. Gastroenterology 12 (1977) 841-847
Salvioli, G. et al. Gut 19 (1978) 844-850
Gaskina, T.K. et al. Voprosy meditsinskoi khimii 331 (1987) 96-99
Cell Membranes
Ehrly, A.M. Report no. 842276 of March 17, 1975 – and R. Blendin in: Phosphatidylcholine, H. Peeters (ed.) Springer Berlin 1976, 228-236
Blagosklonov, A.S. et al. Kardiologiya 26 (1986) 35-38
3 Nei’mark Al, Zhukov, VN et al. Use of isradipine and EPL for protection of the kidney during extracorporeal lithotripsy
Urologiia I Nefrologiia. (6):19-21, 1998 Nov-Dec
4 Kuntz, E. The “essential” phospholipids in hepatology – 50 years of experimental and clinical experiences
Z Gastroenterol (Suppl 2) 1991: 29:7-13